
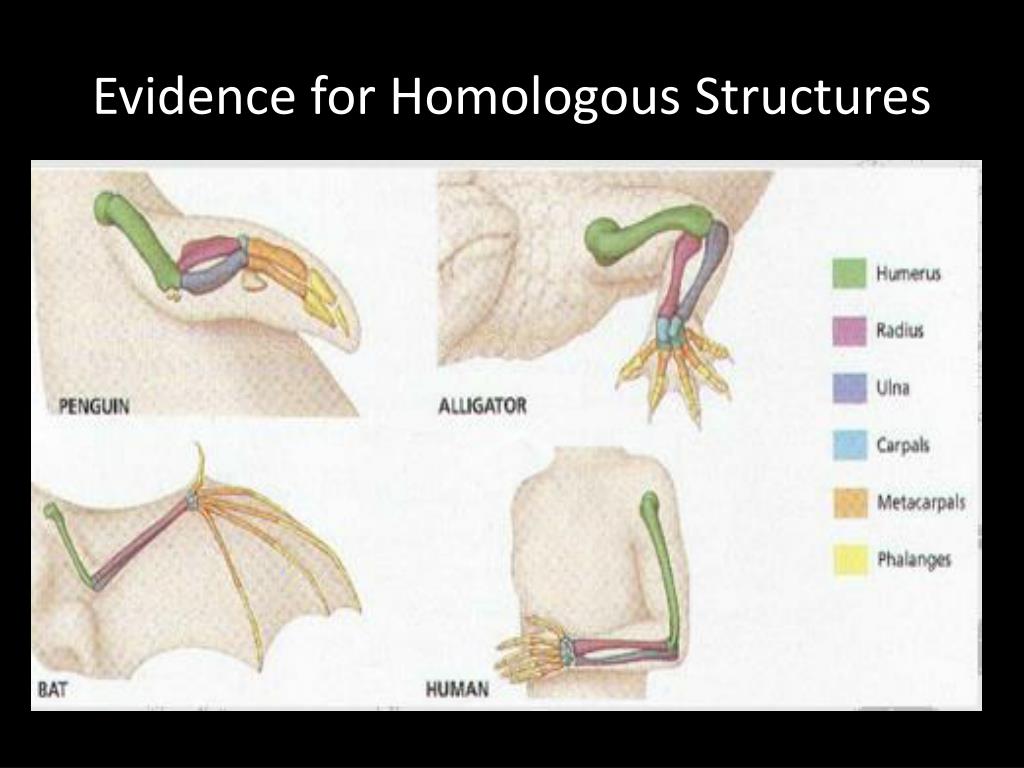
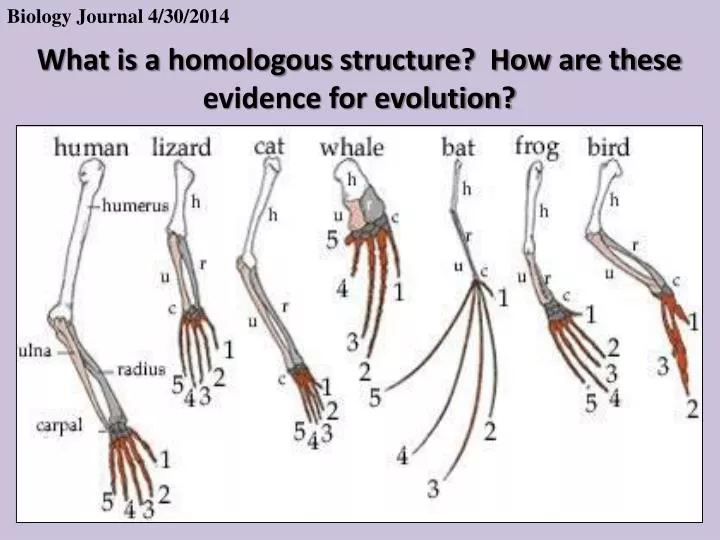
Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs).
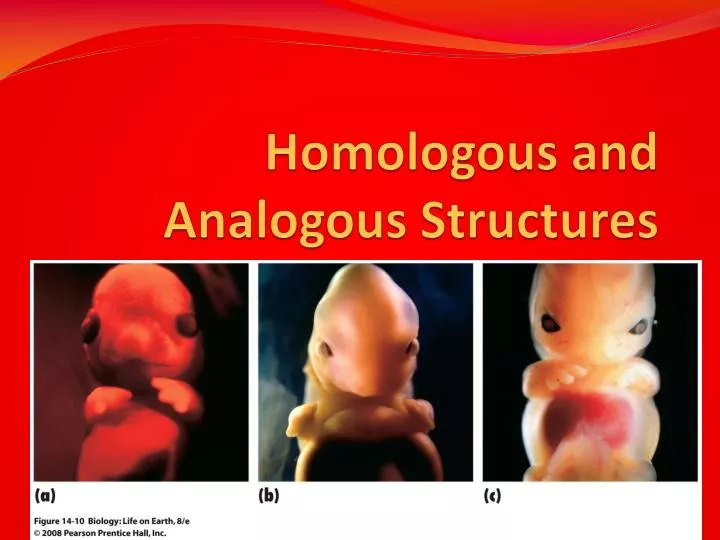
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. coli), a gene has a similar function ( histone-like nucleoid-structuring protein) but has a separate evolutionary origin and so is an analog. A speciation event produces orthologs in the two daughter species (human and chimpanzee). Top: An ancestral gene duplication produces two paralogs ( histone H1.1 and 1.2).
Gene phylogeny as red and blue branches within grey species phylogeny.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
